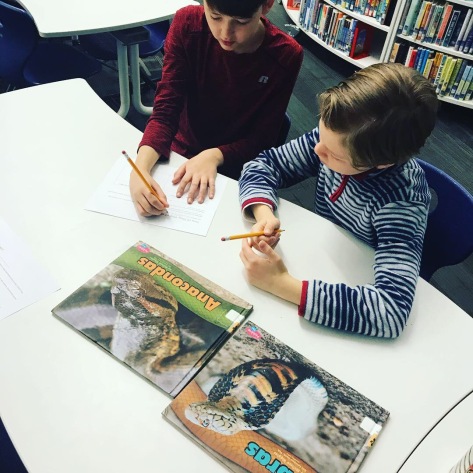
Our 3rd grade is currently learning about the plants, animals, and habitats in the 5 regions of Georgia. The teachers wanted students to have an opportunity to gather some background knowledge prior to their lessons in the classroom, so I worked on a series of centers for students to rotate through and experience these standards in a variety of formats.
S3L1. Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information about the similarities and differences between plants, animals, and habitats found within geographic regions (Blue Ridge Mountains, Piedmont, Coastal Plains, Valley and Ridge, and Appalachian Plateau) of Georgia.
- a. Ask questions to differentiate between plants, animals, and habitats found within Georgia’s geographic regions.
- b. Construct an explanation of how external features and adaptations (camouflage, hibernation, migration, mimicry) of animals allow them to survive in their habitat.
- c. Use evidence to construct an explanation of why some organisms can thrive in one habitat and not in another.
S3E2. Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information on how fossils provide evidence of past organisms.
- a. Construct an argument from observations of fossils (authentic or reproductions) to communicate how they serve as evidence of past organisms and the environments in which they lived.
- b. Develop a model to describe the sequence and conditions required for an organism to become fossilized. (Clarification statement: Types of fossils (cast, mold, trace, and true) are not addressed in this standard.)

To make instructions easy to access, I put everything on a Google doc with a short link. As each class arrived to the library, I split the class into groups of 3-4 students by having them sit on color dots on the floor. We briefly talked about the main goal of the standards being to compare and contrast the plants, animals, and habitats of the 5 regions of Georgia, and then I sent color dot groups to centers. I kept a timer on my phone for 8-10 minutes per center and students rotated to the next center in number sequence.
Center 1

Georgia Public Broadcasting has an amazing set of virtual tours on a whole range of science and social studies standards. For this center, students explored the physical features of Georgia including the Okefenokee Swamp, fall line, various mountains, Providence Canyon, and the Barrier Islands. The purpose of this center was for students to explore the physical features through pictures, maps, text, and video and think about what adaptations plants and animals might need in order to live in these areas of Georgia.
Center 2

In addition to regions, students learn about fossils and how those fossils tell us about the past. At this station, I wanted students to see that fossils aren’t just about dinosaurs and that we have fossil discoveries right her in Georgia. Students visited a Georgia fossil site which includes a map of where fossils have been found and what time period they are from.

The site also included lots of text to skim and scan for details about what was learned from the fossils. Students also had access to several books from our library about fossils and how they teach us about the past.
Center 3

This center featured another GPB virtual tour. This one focused on the 5 regions of Georgia. Students could visit as many regions as time allowed and read the text, look at pictures, and watch videos to identify animals and plants that live in each region. Students could also look at the land and see the possible habitats in each region.
Center 4

Since a piece of the standard is about comparing and contrasting, this book featured print books about the regions and habitats of Georgia. Students chose 2 books, which were about 2 different areas of Georgia.

As they read and looked at photographs, they thought about what was the same and different about the 2 regions.
Center 5

This center had the most pieces but the most popular part of this center was looking at various posters that featured groups of animals in Georgia. There was a poster for bats, snakes, salamanders, dragonflies, lizards, and butterflies as well as a poster of plants.

On the back of the poster, students could see a highlighted map for each plant or animal that showed where it could be found in Georgia. Students identified plants and animals found in specific regions as well as ones that could be found in all regions. If students found a particular animal they were interested, they could use the computer to research more info on that animal. I included links for various animal groups to get them started.
- Butterflies/Moths https://www.butterfliesandmoths.org
- Dragonflies https://www.insectidentification.org/
- Lizards https://srelherp.uga.edu/lizards/index.htm
- Salamanders https://srelherp.uga.edu/salamanders/index.htm
- Snakes https://georgiawildlife.com/georgiasnakes
I also included some books about animal adaptations such as camouflage, hibernation, and migration.

Teacher Role
In each session, the teachers and I rotated around to all the centers to have conversations with individuals or groups of students. We helped students focus on the question of each center and asked follow up questions as needed. I loved seeing what each student was discovering and having me plus a couple of teachers helped us have many conversations. This format had structure, but it also gave students freedom to choose what interested them at each center to spend the most time on. The timing was also fast-paced so there was no time to be bored or be “done”.

When students finished visiting all 5 centers, we came back together on the carpet and students had a chance to share some of the most interesting things that they discovered. Overall, this format served its purpose of gathering background information and it held closely to the wording of the standards. I loved that students were able to explore the standards in a variety of formats and there was variety from one center to the next. This is something I would definitely repeat, but I do wonder about what might be added to help students remember some of the interesting nuggets of information they learned along the way. I wouldn’t want to add too much writing because that slows down the gathering of background knowledge, but it would be nice to have some means for remembering a few facts.
If you have ideas or you try this and add something new, please leave a comment.
















 Killer Whale vs. Great White Shark. T-Rex vs. Velociraptor. Scorpion vs. Centipede. These topics grab the attention of so many readers in our library.
Killer Whale vs. Great White Shark. T-Rex vs. Velociraptor. Scorpion vs. Centipede. These topics grab the attention of so many readers in our library.